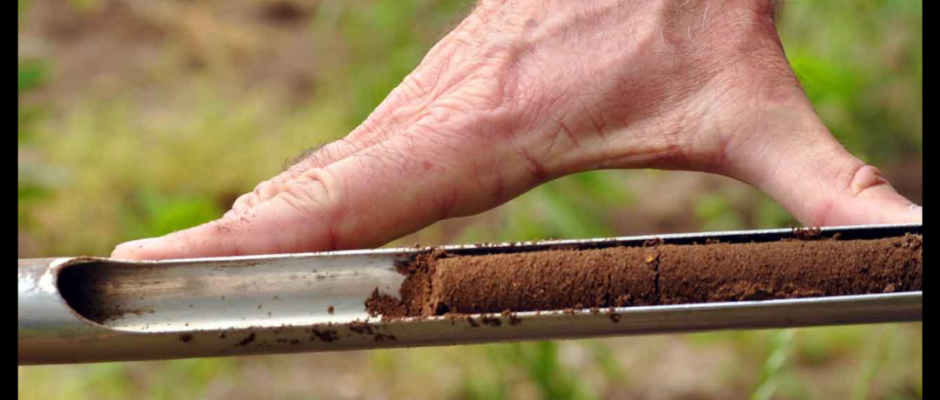
Soil investigation is a fundamental and indispensable process in civil engineering, infrastructure development, and construction projects. Before constructing any structure—whether a residential building, commercial complex, industrial facility, bridge, road, or large-scale infrastructure—a clear understanding of soil and subsurface conditions is essential.
Soil investigation provides critical information about the physical, chemical, and mechanical properties of soil. This data enables engineers to design foundations that are safe, economical, durable, and compliant with engineering standards.
In today’s rapidly urbanizing environment, construction is expanding across cities, towns, and semi-urban regions. Since soil conditions vary significantly from one location to another due to geology, climate, groundwater levels, and human activity, soil investigation is not just a preliminary step—it is a core engineering requirement that directly impacts project safety and success.
What is Soil Investigation?
Soil investigation, also known as geotechnical investigation, is the systematic study of soil, rock, and groundwater conditions at a proposed construction site. Its primary objective is to evaluate whether the ground can safely support the planned structure and to identify potential geotechnical risks.
These risks may include:
-
Excessive settlement
-
Bearing capacity failure
-
Slope instability
-
Liquefaction
-
Groundwater-related issues
The process includes field exploration, soil sampling, laboratory testing, and geotechnical analysis. The results are compiled into a soil investigation report that provides foundation design recommendations and construction guidelines.
Importance of Soil Investigation in Construction Projects
A well-planned soil investigation plays a decisive role in the planning and design stages of any construction project. Inadequate or ignored soil investigation can lead to structural damage, financial loss, and safety hazards.
1. Foundation Safety and Stability
The foundation transfers the structural load to the ground. Soil investigation determines whether the soil has adequate strength and stiffness to carry these loads without failure or excessive settlement.
2. Cost Optimization
Accurate soil data helps engineers select the most economical foundation type. Overdesign increases unnecessary costs, while underdesign can cause future repairs and structural distress.
3. Risk Identification and Mitigation
Problematic soil conditions such as expansive soils, loose sands, soft clays, collapsible soils, or high groundwater levels are identified early, allowing engineers to plan suitable ground improvement measures.
4. Compliance with Codes and Standards
Most national and international building codes mandate soil investigation before structural design. Proper investigation ensures regulatory compliance and smooth approval from authorities.
Scope of Soil Investigation Services
A comprehensive soil investigation program generally includes the following stages:
1. Site Reconnaissance
Initial site inspection to study topography, surface conditions, drainage patterns, accessibility, and nearby structures. This helps in planning the investigation approach.
2. Field Exploration
Field exploration is carried out to examine subsurface soil layers using methods such as:
-
Borehole drilling
-
Standard Penetration Test (SPT)
-
Dynamic Cone Penetration Test (DCPT)
-
Plate Load Test
The number and depth of boreholes depend on the project type and size.
3. Soil Sampling
Both disturbed and undisturbed soil samples are collected during drilling to accurately evaluate soil properties.
4. Laboratory Testing
Laboratory tests are conducted to determine:
-
Grain size distribution
-
Atterberg limits
-
Moisture content
-
Bulk density
-
Shear strength parameters
-
Consolidation characteristics
These tests help classify soil and assess its engineering behavior.
5. Geotechnical Analysis and Reporting
All field and laboratory data are analyzed to prepare a detailed soil investigation report. The report typically includes:
-
Soil stratification
-
Groundwater level
-
Safe bearing capacity
-
Settlement analysis
-
Foundation recommendations
Soil Investigation for Different Types of Projects
Soil investigation requirements vary based on the nature of the project:
-
Residential Buildings: Bearing capacity and settlement control
-
Commercial & High-Rise Buildings: Deep foundation analysis and load behavior
-
Industrial Projects: Heavy loads, vibration, and machinery effects
-
Roads & Highways: Subgrade evaluation and pavement design
-
Bridges & Flyovers: Deep strata investigation and scour analysis
-
Water & Sewerage Projects: Soil permeability and trench stability
Each project demands a customized investigation approach to ensure safety and performance.
Soil Investigation in Different Cities
Soil conditions vary significantly from city to city due to differences in geology, terrain, and groundwater levels. Urban areas may contain filled or disturbed soils, while developing regions often have natural deposits with varying strengths.
We provide professional soil investigation services across multiple cities, adapting methodologies to suit local soil conditions and project requirements. Our experience in metropolitan cities, tier-2 cities, and industrial zones ensures reliable data collection and accurate geotechnical recommendations for every site.
Role of Soil Investigation in Sustainable Construction
Soil investigation plays a vital role in sustainable construction by:
-
Optimizing foundation design and reducing material wastage
-
Minimizing unnecessary excavation and environmental impact
-
Increasing the lifespan of structures
-
Supporting safe redevelopment and urban expansion
Accurate soil data leads to smarter engineering decisions aligned with long-term sustainability goals.
Challenges in Urban Soil Investigation
Urban soil investigation presents unique challenges, including:
-
Limited site access
-
Underground utilities and services
-
Noise and vibration restrictions
-
Filled or contaminated soils
Experienced soil investigation professionals use advanced equipment and planned methodologies to overcome these challenges while maintaining safety and accuracy.
Why Professional Soil Investigation Services Matter
Soil investigation is a specialized engineering activity that requires technical expertise, modern equipment, and strict adherence to standards. Professional service providers ensure:
-
Accurate field data collection
-
Standard laboratory testing
-
Expert geotechnical interpretation
-
Clear, actionable soil investigation reports
Soil investigation is the backbone of safe, economical, and successful construction. It provides essential insights into subsurface conditions, enabling engineers to design foundations that perform reliably over time.
As construction activities continue to expand across cities and regions, the demand for reliable soil investigation services becomes increasingly important. By offering soil investigation services in different cities, we support infrastructure and construction projects with accurate geotechnical data and expert recommendations—ensuring every project starts with a strong foundation, both technically and structurally.